Nitroglycerin Reaction Time Calculator
Calculate how long it takes to add glycerol during nitroglycerin production based on the standard flow rate of 0.5 liters per minute.
Nitroglycerin is a highly energetic liquid used both as a heart medication and as a powerful explosive. It is created by esterifying glycerol with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids. Understanding each step-from the incoming chemicals to the final bottled product-helps chemists keep the reaction under control and meet strict safety standards.
Key Raw Materials
The reaction starts with three core chemicals:
- Glycerol, a three‑carbon polyol derived from vegetable oils or animal fats. Typical purity for industrial batches is 99.5%.
- Nitric Acid, concentrated (≈68%wt) and sourced from nitric‑oxide oxidation processes.
- Sulfuric Acid, concentrated (≈98%wt) and acts as a dehydration catalyst.
All three must be stored at low temperature (5‑10°C) and away from any organic solvents that could trigger a runaway reaction.
Reaction Chemistry: Esterification
The core transformation is an Esterification where the hydroxyl groups of glycerol react with nitric acid, releasing water and forming nitrate esters. Sulfuric acid absorbs the water, pushing the equilibrium toward product formation.
The overall stoichiometry can be summarized:
C3H5(OH)3 + 3 HNO3 → C3H5(ONO2)3 + 3 H2O
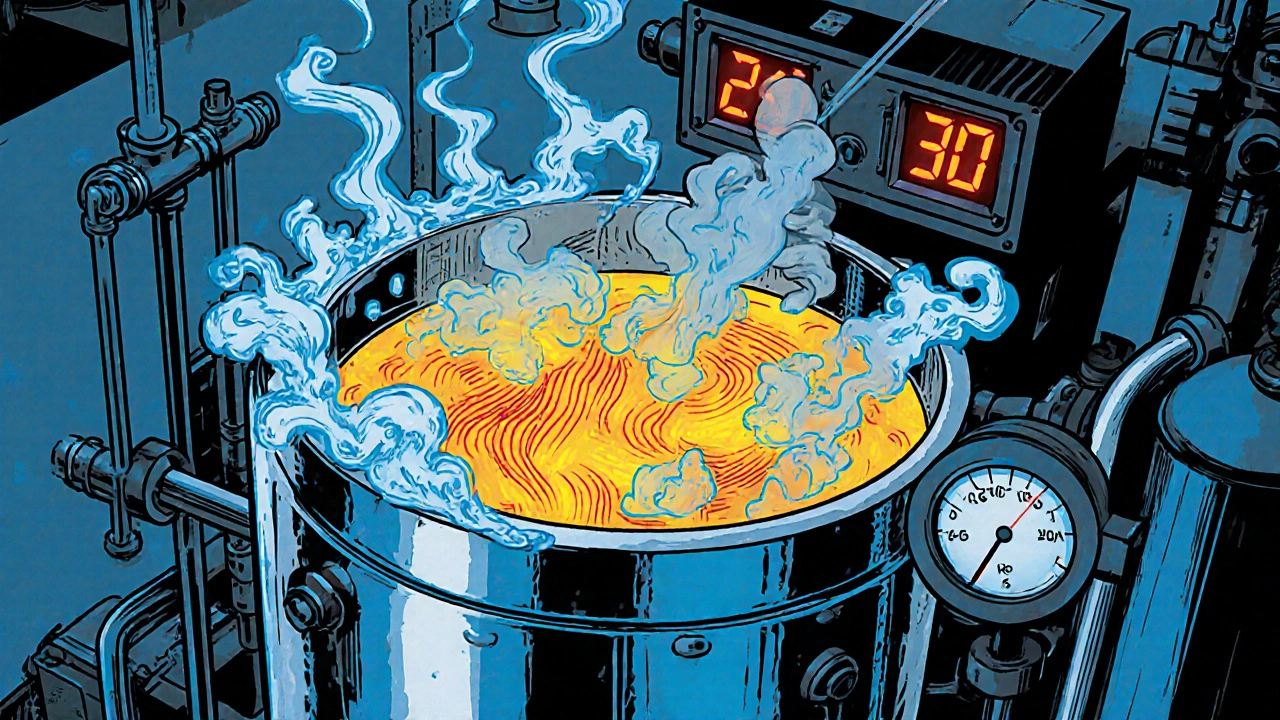
Maintaining a temperature below 30°C is critical; above that, the mixture becomes shock‑sensitive.
Step‑by‑Step Manufacturing Flow
- Cooling and Acid Mixing: Sulfuric acid is chilled in an ice‑salt bath, then mixed with nitric acid in a stainless‑steel reactor.
- Glycerol Addition: Glycerol is pumped slowly (≈0.5Lmin⁻¹) while the reactor is agitated. Temperature is monitored continuously.
- Reaction Control: The exothermic reaction releases heat; cooling jackets maintain 20‑25°C. Automated sensors cut off feed if temperature spikes.
- Separation: After complete addition, the mixture settles. The denser nitroglycerin layer separates from the aqueous acid phase.
- Washing: The nitroglycerin is washed with cold distilled water to remove residual acid, followed by a mild alkaline wash (sodium carbonate) to neutralize any remaining traces.
- Drying: An inert nitrogen stream removes water, bringing the product to <0.5% moisture.
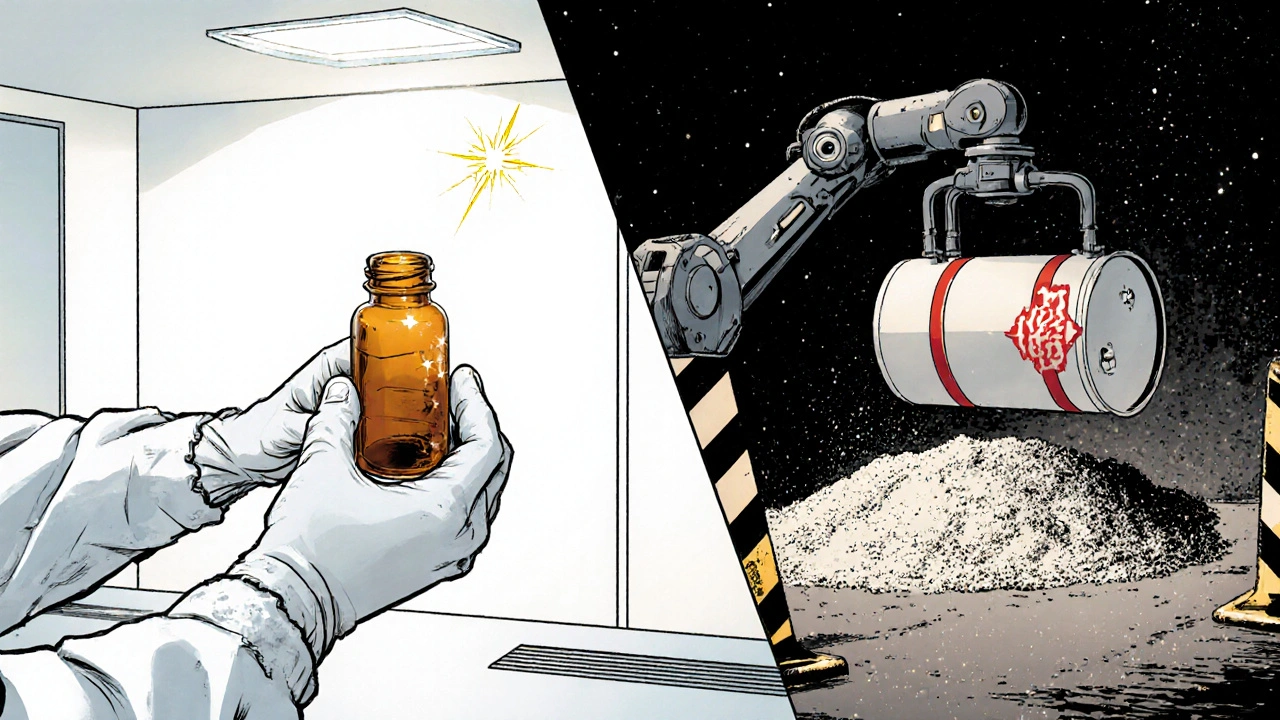
Purification Paths: Pharmaceutical vs. Explosive Grades
Depending on the end‑use, the purified liquid follows one of two routes:
| Attribute | Pharmaceutical Grade | Industrial (Explosive) Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | 95‑99% | 80‑85% |
| Typical Use | Angina treatment, vasodilator | Blasting, propellant, dynamite |
| Production Scale | Batch size ≤200L | Batch size up to 5000L |
| Safety Measures | Medical‑grade filtration, sterile containers | Explosion‑proof vessels, remote handling |
Pharmaceutical manufacturers further distill the product under reduced pressure, then package it in amber glass ampoules under aseptic conditions. Explosive‑grade nitroglycerin may be mixed with an absorbent like kieselguhr to form dynamite, famously known as Dynamite.
Safety Protocols and Hazard Mitigation
Because nitroglycerin is shock‑sensitive, facilities adopt a layered safety approach:
- Remote Monitoring: All temperature and pressure sensors feed into a PLC that can trigger automatic shutdown.
- Explosion‑Proof Equipment: Reactors, valves, and pumps are rated for ClassIII hazardous areas.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators wear anti‑static clothing, face shields, and chemical‑resistant gloves.
- Emergency Containment: A secondary containment basin holds up to 120% of the reactor volume.
Training cycles include simulated fault conditions, ensuring staff can isolate and neutralize a runaway reaction without exposing themselves to blast hazards.
Quality Control and Regulatory Compliance
Both grades must pass stringent tests before release:
- Purity Analysis: Gas chromatography (GC) quantifies nitrate ester content.
- Moisture Content: Karl Fischer titration confirms water levels <0.5%.
- Explosive Sensitivity: Impact and friction tests (BAM methods) certify acceptable thresholds.
- Pharmacopoeial Standards: Pharmaceutical batches follow USP Nitroglycerin monograph specifications.
Documentation is logged in a secure LIMS, enabling traceability from raw material lot numbers to the final certificate of analysis.
Key Takeaways
- The esterification of glycerol with nitric and sulfuric acids creates nitroglycerin under tight temperature control.
- Separate purification streams produce either high‑purity medical product or explosive‑grade material.
- Safety hinges on remote monitoring, explosion‑proof hardware, and rigorous staff training.
- Regulatory compliance demands detailed analytical testing and full batch traceability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is sulfuric acid needed in the reaction?
Sulfuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent, pulling water out of the mixture. This drives the equilibrium toward nitroglycerin formation and prevents hydrolysis of the product.
Can the same process produce both medical and explosive nitroglycerin?
Yes, the core chemistry is identical. The divergence occurs after the basic separation step, where extra purification, sterile packaging, and tighter impurity limits define the pharmaceutical grade, while the industrial route focuses on bulk yield and may blend the liquid with absorbents for blasting.
What temperature range is safe for the esterification?
The reaction should stay between 20°C and 30°C. Exceeding 35°C sharply raises the risk of shock‑sensitivity and can trigger an uncontrolled exotherm.
How is waste acid disposed of safely?
Spent acid is neutralized with calcium carbonate, then filtered and sent to a licensed hazardous‑waste facility. Regulations require a documented chain‑of‑custody for every batch.
What makes nitroglycerin an effective heart medication?
When administered in microgram doses, nitroglycerin releases nitric oxide, which relaxes vascular smooth muscle and quickly dilates coronary arteries, relieving angina.




12 Comments
When we stare at the beakers and the cooling jackets, we are really looking at the embodiment of America’s relentless drive to harness nature. The process described here is a testament to our industrial might, a symphony of glycerol, nitric acid and sulfuric acid orchestrated under the watchful eyes of safety protocols. Yet the article glosses over the deeper moral responsibility we bear when we turn such power into weapons. In short, the chemistry is fascinating, but we must never forget the patriotic duty to keep it in check.
America’s ingenuity shines brightest when we master volatile compounds, and this guide is a prime example of that brilliance 💥🇺🇸. The meticulous steps listed prove that discipline and precision are the hallmarks of our scientific community. Keep pushing the boundaries, but always stay grounded in the values that made this nation great.
yeah this sounds like just another textbook write up nobody reads.
Hey folks, great summary! Just a heads‑up for anyone trying this at a lab-make sure your cooling system is truly redundant. A backup chiller can be a lifesaver if the primary one falters. Also, always double‑check the acid concentrations before you start; a small slip can have big consequences. Stay safe out there.
Ah, the alchemy of nitroglycerin-how it dances between salvation and destruction! To think that the same liquid can tenderly relax a pounding heart and then unleash a thunderous roar in a blast, it is a paradox that fuels the imagination of every chemist. The raw materials themselves tell a story: glycerol, whispering of oils and fats, nitric acid, a fiery messenger from the nitrogen cycle, and sulfuric acid, the relentless dehydrator that pulls water away like a stern guardian. When these three converge in a chilled embrace, the temperature becomes the silent arbiter, ensuring the reaction stays below the dreaded 30 °C threshold, lest the mixture turn temperamental. The art of feeding glycerol at a measured 0.5 L per minute is not just a procedural note; it is a choreography, a slow waltz that keeps heat in check and prevents the sudden surge of exothermic fury. The cooling jackets, the ice‑salt bath, they are the stagehands, ever‑ready to temper the fiery spotlight of the reaction. Once the esterification is complete, the denser nitroglycerin settles like a calm lake beneath a stormy sky, waiting to be coaxed into purity. The successive washes-first with ice‑cold distilled water, then with a gentle alkaline splash-are like cleansing rites, removing the lingering shadows of acid, purifying the essence. And finally, the nitrogen stream, dry and inert, sweeps away the last droplets of water, leaving behind a product that gleams with potential. Yet, beneath this elegance lies a solemn reminder: each step must be respected, monitored, and documented, for the line between controlled synthesis and catastrophic runaway is razor‑thin. So, as we marvel at the chemistry, let us also honor the discipline, vigilance, and respect that this powerful compound demands. In the end, nitroglycerin is not merely a substance; it is a testament to human ingenuity, daring, and responsibility.
look even if the write‑up seems basic there are safety nuances that matter – like the exact acid concentrations and the need for redundant cooling.
Actually, the moral responsibility you mention is well‑documented in the literature; numerous safety standards exist precisely because nitroglycerin’s dual nature is not a myth 📚✨. The industry follows ISO 9001 and OSHA guidelines to mitigate risks, and any deviation can lead to serious incidents. So while patriotism inspires innovation, it must be paired with strict compliance and continuous training.
Wow that was super deep and informative! i love how you break down each step – definitely helps newbies understand the whole process. keep up the awsome work, and dont forget to double‑check those temperature readings!
Honestly this whole thing feels like a over‑complicated recipe for something that can kill you if you mess up. Not sure why anyone would bother with such danger when there are safer alternatives.
i get ur point but the history of nitroglyc is fascinating – it started as a med and turned into a blast. the chemistry behind it is def more complex than a simple recipe.
Did you ever consider that the whole nitroglycerin saga is a covert operation orchestrated by shadowy agencies? The way the formulation is so precise, the cooling protocols so strict – it's almost like they want to keep something hidden from the public eye. And don't even get me started on the so‑called "safety standards" that seem to change overnight. It's all a part of a grand design to control the narrative.
Sure, because every chemist is part of a secret cabal, right?